Empowering Adolescents: Understanding Youth Suicide and Mental Health Education
Empowering Adolescents: Understanding Youth Suicide and Mental Health Education
Read Disclaimer
Empower adolescents by understanding youth suicide and implementing comprehensive mental health education. Learn about risk factors, support systems, coping strategies, and the role of peer advocacy.
Introduction:
Adolescence is a pivotal period of transition marked by numerous physical, emotional, and social changes. While this phase is often associated with growth and self-discovery, it also presents significant challenges, particularly concerning mental health. Suicide among adolescents is a pressing concern worldwide, highlighting the critical need for effective mental health education and support systems. Empowering adolescents with the knowledge and resources to understand and address mental health issues is paramount in preventing tragedies and fostering well-being. This article delves into the intricacies of youth suicide and the importance of mental health education in empowering adolescents.

Understanding Youth Suicide:
Youth suicide is a complex and multifaceted issue influenced by various factors, including psychological, social, and environmental elements. Adolescents facing mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse are at a heightened risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Additionally, experiences of bullying, trauma, familial conflicts, and societal pressures can exacerbate feelings of hopelessness and isolation, further contributing to suicidal ideation.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), suicide is the fourth leading cause of death among individuals aged 15 to 19 years globally. Alarmingly, suicide rates among adolescents have been on the rise in many countries, underscoring the urgent need for preventive measures and intervention strategies.
One of the critical aspects of addressing youth suicide is recognizing the warning signs and risk factors. These may include sudden changes in behavior, withdrawal from social activities, expressions of despair or worthlessness, substance abuse, and giving away prized possessions. By understanding these indicators, parents, educators, and peers can intervene early and provide the necessary support and intervention.
Mental Health Education: A Crucial Intervention:
Effective mental health education plays a pivotal role in equipping adolescents with the knowledge, skills, and support networks necessary to navigate the challenges they face. Integrating comprehensive mental health education into school curricula is essential in promoting awareness, reducing stigma, and fostering early intervention.
First and foremost, mental health education should encompass a wide range of topics, including stress management, emotional regulation, coping strategies, and interpersonal skills. By providing adolescents with practical tools to manage their emotions and navigate difficult situations, they can develop resilience and better cope with the pressures of adolescence.
Moreover, mental health education should address the stigma surrounding mental illness, promoting empathy, understanding, and acceptance. Creating a safe and supportive environment where students feel comfortable discussing their feelings and seeking help is crucial in breaking down barriers to mental health care.
In addition to classroom-based education, schools should implement comprehensive mental health support systems that provide access to counselors, psychologists, and other mental health professionals. These professionals play a vital role in identifying at-risk students, providing counseling services, and facilitating referrals to appropriate mental health resources in the community.
Furthermore, parents and caregivers play a crucial role in supporting adolescent mental health. Providing open communication channels, offering unconditional support, and modeling healthy behaviors are essential in promoting positive mental well-being within the family unit.
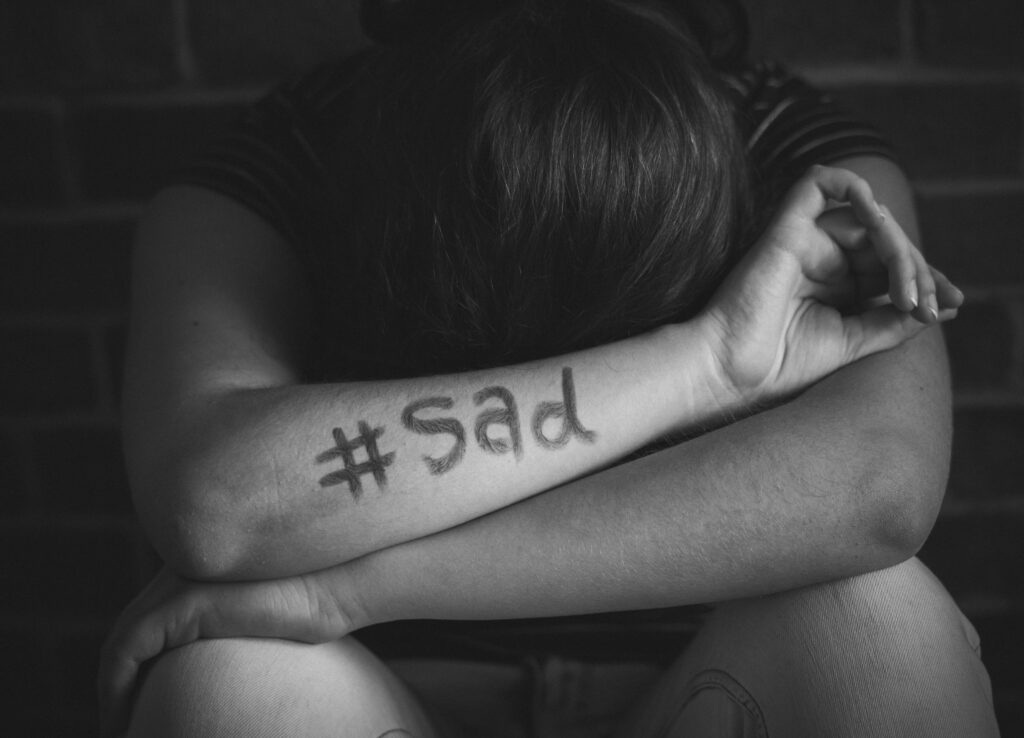
The Role of Peer Support and Youth Advocacy:
Peer support programs and youth advocacy initiatives are powerful tools in promoting mental health awareness and resilience among adolescents. Peer support groups provide a safe space for young people to share their experiences, seek advice, and receive support from their peers who may be facing similar challenges.
Moreover, youth advocacy programs empower adolescents to become agents of change in their communities by raising awareness about mental health issues, advocating for policy changes, and promoting access to mental health services. Engaging adolescents in advocacy efforts not only amplifies their voices but also fosters a sense of empowerment and ownership over their mental health and well-being.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While progress has been made in advancing mental health education and support services for adolescents, significant challenges remain. Limited resources, stigma, and cultural barriers continue to impede access to mental health care for many young people worldwide. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from policymakers, educators, healthcare professionals, and community stakeholders.
Furthermore, the digital age presents both opportunities and challenges in addressing adolescent mental health. While technology can facilitate access to information and support networks, it also poses risks such as cyberbullying, social media addiction, and exposure to harmful content. Thus, it is essential to incorporate digital literacy and responsible technology use into mental health education programs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, addressing youth suicide and promoting mental health education among adolescents are critical endeavors that require collective action and commitment from various stakeholders. By understanding the complex interplay of factors contributing to youth suicide, including mental health challenges, social pressures, and environmental stressors, we can better equip adolescents with the tools and support they need to navigate these challenges successfully.
Comprehensive mental health education, integrated into school curricula and supported by accessible mental health services, plays a pivotal role in empowering adolescents to recognize warning signs, seek help, and build resilience. Creating a culture of acceptance, empathy, and support for those facing mental health issues is essential in reducing stigma and promoting early intervention.
Moreover, peer support programs and youth advocacy initiatives are valuable resources in promoting mental health awareness and resilience among adolescents. By fostering peer connections and empowering young people to become advocates for change, we can amplify voices, break down barriers, and create inclusive environments where every young person feels valued and supported.
While challenges such as limited resources, stigma, and digital risks persist, ongoing efforts to prioritize adolescent mental health and well-being are essential. Through collaborative action, education, advocacy, and support, we can work towards a future where youth suicide rates decline, and all adolescents have the opportunity to thrive mentally, emotionally, and socially.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) with Answers:
- What are the common risk factors for youth suicide?
– Common risk factors include mental health disorders, substance abuse, trauma, bullying, and social isolation.
- How can parents support their adolescent’s mental health?
– Parents can support their adolescent’s mental health by fostering open communication, providing unconditional support, and modeling healthy behaviors.
- What role do schools play in addressing youth suicide?
– Schools play a crucial role by integrating mental health education into curricula, providing access to counselors, and fostering supportive environments.
- How can adolescents recognize warning signs of suicide in themselves or others?
– Adolescents can recognize warning signs such as changes in behavior, expressions of hopelessness, and withdrawal from social activities.
- What are some effective coping strategies for managing stress and emotions?
– Effective coping strategies include mindfulness, physical activity, seeking social support, and engaging in creative outlets.
- How can peer support groups benefit adolescents’ mental health?
– Peer support groups provide a safe space for adolescents to share experiences, seek advice, and receive support from their peers facing similar challenges.
- What are the impacts of stigma on adolescent mental health?
– Stigma can discourage adolescents from seeking help, exacerbate feelings of shame and isolation, and contribute to negative self-esteem.
- How can digital technology impact adolescent mental health?
– Digital technology can facilitate access to information and support networks but also pose risks such as cyberbullying and social media addiction.
- What resources are available for adolescents experiencing mental health challenges?
– Resources include school counselors, mental health hotlines, support groups, and online resources like helplines and informational websites.
- What role can youth advocacy play in promoting mental health awareness?
– Youth advocacy empowers adolescents to raise awareness, advocate for policy changes, and promote access to mental health services in their communities.
- How can educators incorporate mental health education into their classrooms?
– Educators can integrate mental health education into existing curricula, incorporate guest speakers, and facilitate discussions on mental health topics.
- What are some signs that an adolescent may be struggling with their mental health?
– Signs may include changes in mood, appetite, sleep patterns, academic performance, and social interactions.
- What are the long-term effects of untreated mental health issues in adolescence?
– Untreated mental health issues can lead to academic difficulties, substance abuse, relationship problems, and increased risk of suicide.
- How can communities support adolescent mental health initiatives?
– Communities can support initiatives by raising awareness, advocating for resources, and fostering partnerships between schools, healthcare providers, and community organizations.
- What steps can individuals take to promote their own mental well-being?
– Individuals can promote their mental well-being by prioritizing self-care, seeking support when needed, and engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment.

Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/kz/register?ref=RQUR4BEO
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/ar-BH/register-person?ref=V2H9AFPY
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? binance
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
PP, WM, EVO, DG, AG, Microgaming, SA, VIVA Gaming,… xn88 có uy tín không các NPH Live Casino tiềm năng mang đến cho người chơi hàng loạt cơ hội nhận thưởng gấp 40 lần tiền cược ban đầu. Bạn có thể thử sức với các trò chơi mới lạ như: Fast Baccarat, Speed Roulette, Fan Tan,… TONY12-26
Also, we check if they have reasonable, fair, and easy wagering requirements.
Every casino must show proof of an RNG (random number generator) certificate.
We can confirm every casino platform we recommend on our website is completely secure.
As we have already discussed, this bonus can either be free bonus credit or
free spins. The terms and conditions of the bonus will contain all
these details.
So let’s review the most important conditions to watch for when claiming casino bonuses, including no deposit bonuses.
These bonuses provide extra credits to your account, allowing you
to explore real-money casino games without any initial
investment. You can also use our filter ‘Bonuses for’ to only find
no deposit bonuses for new players or for existing players.
No deposit casino bonuses come with many rules and restrictions, such as maximum bet limits and
wagering requirements. Many online casinos offer different promotions depending on where you’re playing from.
References:
ufo9
online poker real money paypal
References:
https://kigalilife.co.rw/author/maggiedorma/
australian online casinos that accept paypal
References:
interior01.netpro.co.kr
online slot machines paypal
References:
https://www.securityprofinder.com/employer/best-payout-online-casinos-with-97-rtp-december-2025/
casino avec paypal
References:
https://healthcarejobies.com/employer/complete-list-2025/
Sie bietet eine verlässliche Übersicht über seriöse und lizenzierte Anbieter, die hohe Sicherheitsstandards, faire Spielbedingungen und einen umfassenden Spielerschutz gewährleisten. Echtgeldspiele bieten dabei nicht nur Spannung, sondern auch die Chance auf echte Gewinne und schnelle Auszahlungen. Für deutsche Spieler ist es daher essenziell, eine verlässliche Online Casinos Bestenliste zu nutzen, die nur seriöse und lizenzierte Anbieter enthält. Dabei sollten die gelisteten Casinos eine Top Auswahl an Casino Spielen, insbesondere Online Slots und andere beliebte Casinospiele, bieten. Eine gute Online Casinos Liste bietet eine übersichtliche Darstellung von Online Casino Seiten, die eine deutsche Lizenz besitzen und somit legal in Deutschland agieren dürfen.
Viele Slots enthalten Bonusfunktionen wie Freispiele, Multiplikatoren und Wild-Symbole. Diese Spiele bieten verschiedene Themen, von klassischen Früchte-Slots bis zu modernen Video-Slots mit aufwendigen Grafiken. Sichere Online Casinos arbeiten nur mit bekannten und vertrauenswürdigen Zahlungsanbietern zusammen. Eine gültige Glücksspiellizenz ist das wichtigste Merkmal eines seriösen Online Casinos. Spielerschutz-Programme bieten Einzahlungslimits und Selbstausschluss-Optionen.
References:
https://onlinegamblingcasino.s3.amazonaws.com/casino%20royal%20outfit%20damen.html
Tischspiele wie Roulette und Co. sowohl als auch Jackpots und Live Dealer Spiele werden momentan nicht angeboten. Die besten Online Casinos in Deutschland bieten neben einer großen Auswahl an beliebten Spielen auch hohe Gewinnchancen an. Denn seien wir ehrlich, wer mag kein extra Geld oder kostenlose Freispiele? Seit 2021 können deutsche Online Casinos Lizenzen von der GGL (Gemeinsame Glücksspielbehörde der Länder) erwerben. Sobald das Guthaben gutgeschrieben ist, kannst du deine Lieblingsspiele starten und erste Gewinne erzielen. Die deutsche Casino Landschaft verändert sich ständig.
Diese sind in Online Casinos für Deutschland zu finden, die durch europäische Glücksspiellizenzen abgesichert sind. Da der deutsche Glücksspielmarkt sehr streng reguliert ist, suchen viele Spieler nach passenden Ausweichmöglichkeiten. Im Jahr 2021 trat der neue Glücksspielstaatsvertrag in Kraft, der eine einheitliche Regulierung für Online Glücksspielanbieter in Deutschland einführte. In den Anfangsjahren waren viele Online Casinos Deutschland nicht lizenziert und operierten in einer rechtlichen Grauzone.
References:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/onlinegamblingcasino/rtp%20casino.html
Allerdings kann es sein, dass Sie mit dem Verfahren ein wenig Schwierigkeiten haben, vor allem, wenn Sie zum ersten Mal in einem Online Casino spielen. Sie können jedes beliebige Spiel wie Roulette, Blackjack und Baccarat auswählen und vor Ort mitspielen! Sie können alle Spiele kostenlos im Demo Modus spielen, ohne sich anzumelden oder Sie können echtes Geld einsetzen, um die echten Emotionen und Gewinne zu erleben (Anmeldung ist hierfür erforderlich). Alle Spiele sind so konzipiert, dass Anfänger und erfahrene Spieler gleichermaßen Freude daran haben.Darüber hinaus können Sie bei HitnSpin auch Live Casino Spiele spielen.
Hitnspin bietet ein attraktives Bonussystem, das sowohl Neukunden als auch treue Spieler in Deutschland belohnt. Nach erfolgreicher Anmeldung steht Ihnen die komplette Spieleauswahl zur Verfügung. Oben findet man Schaltflächen für Login, Registrierung und Sprachauswahl. Entdecken Sie selbst, was dieses spannende Glücksspielportal zu bieten hat und ob es Ihren persönlichen Vorlieben entspricht. Sie erhalten den Bonus automatisch, wenn Sie Ihre erste Einzahlung im Casino machen. Ja, derzeit gibt es im HitnSpin Casino einen Willkommensbonus für neue Spieler. Vergessen Sie dabei nicht, sich den Willkommensbonus zu sichern!
References:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/onlinegamblingcasino/gewinne%20casino.html
Der Vorteil von Tischspielen liegt darin, dass der Hausvorteil oft geringer ist als bei Slots und geschickte Spieler durch die richtige Strategie ihre Gewinnchancen verbessern können. Bei Tischspielen wie Roulette, Blackjack oder Baccarat werden hingegen nur 15% angerechnet. Wenn Sie also mit einem Grundeinsatz von 0,20€ spielen und die Bonusrunde für 20€ kaufen möchten, würde dies die 5€-Grenze überschreiten und gegen die Bonusbedingungen verstoßen. Obwohl die Bedingungen sehr fair sind, ist es wichtig, sie genau zu kennen, um Missverständnisse zu vermeiden und den Bonus erfolgreich freizuspielen. Dies ist eine bemerkenswert faire und realistische Hürde, die selbst für Gelegenheitsspieler problemlos zu erreichen ist.
Wir haben keine eigene App, aber unsere Website ist vollständig für mobile Geräte optimiert, so dass Sie direkt über den Browser Ihres Smartphones oder Tablets spielen können. Um im Demomodus zu spielen, wählen Sie einfach den Spielautomaten, der Sie interessiert, und klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche “Demo”. Bei Verde Casino bieten wir Ihnen einen attraktiven Willkommensbonus für Sportwetten.
References:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/new-casino/neue%20online%20casinos.html
References:
Argosy casino
References:
https://opensourcebridge.science/wiki/Winz_io
References:
Soaring eagle casino coupons
References:
https://hikvisiondb.webcam/wiki/WD40_Casino_Review_Expert_Player_Ratings_2026
References:
Casino barriere lille
References:
https://www.bitspower.com/support/user/brasswarm4
steroids are a type of
References:
https://zenwriting.net/talkstar30/dianoxyl-10-kalpa-dianabol-methandienone-tablets-usa
References:
Best time to take anavar before or after workout
References:
http://humanlove.stream//index.php?title=jumpersilver6
best steroid cycle for bulking and cutting
References:
https://socialbookmarknew.win/story.php?title=que-ocurre-al-dejar-los-farmacos-adelgazantes-como-ozempic-o-wegovy-el-peso-perdido-suele-volver-euronews
References:
Transformation anavar female before and after
References:
https://ebbesen-aycock-3.thoughtlanes.net/perche-anavar-e-perfetta-per-le-donne
best legal anabolic steroid
References:
https://pads.jeito.nl/s/qiOaBvysN_
steroids uses and side effects
References:
https://king-wifi.win/wiki/Comprar_Dianabol_Metandienona_online_en_Espaa_a_precios_bajos
References:
Women anavar before after
References:
https://able2know.org/user/drivetyvek4/
References:
Anavar before and after 1 month male
References:
https://berrycattle03.bravejournal.net/votre-poulet-roti-est-sec-chaque-dimanche
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://bom.so/yTeVcH
all american steroids review|acybgnsynx72k2lagtrdohjfldslpgzigq:***
References:
https://gpsites.stream/story.php?title=i-migliori-stimolatori-di-testosterone-sul-mercato-2026
References:
Spin games
References:
https://farangmart.co.th/author/printthing3/
References:
Online betting australia
References:
https://opensourcebridge.science/wiki/Online_Casino_Play_Win_Anytime
References:
River rock casino vancouver
References:
http://karayaz.ru/user/georgeclimb34/
References:
Bitcoin casino
References:
https://gratisafhalen.be/author/mexicomenu16/
References:
Uk online casino
References:
https://www.generation-n.at/forums/users/chillleek3/
References:
Sbg global mobile
References:
https://apunto.it/user/profile/568451
References:
Casinos austria
References:
https://doodleordie.com/profile/branchtaste80
References:
Red wind casino
References:
https://lovebookmark.win/story.php?title=candy-casino-built-around-flexible-payments-not-big-cashouts
References:
Blackjack driveway sealer
References:
https://md.un-hack-bar.de/s/PHMsNreJdA
References:
Great northern casino
References:
https://trade-britanica.trade/wiki/Candy96_Casino_Australia_Pokies_Bonus_Deals_Fast_Withdrawals
References:
Valley view casino center seating chart
References:
https://md.swk-web.com/s/rVS_NA_af
References:
Ameristar casinos
References:
https://bookmarks4.men/story.php?title=a-premier-destination-for-real-money-play
References:
Casino sanremo
References:
http://king-wifi.win//index.php?title=notechild33
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://coolpot.stream/story.php?title=digiuno-di-12-18-24-o-36-ore-la-cronaca-minuto-per-minuto-di-glicogeno-chetoni-fame-e-lucidita-cosa-sape
anabolic steroid cream for sale
References:
https://chase-chase.technetbloggers.de/como-aumentar-la-testosterona-de-una-forma-natural
steroids and muscle growth
References:
https://gpsites.stream/story.php?title=testosteron-online-kaufen-in-deutschland-guenstiger-preis-fuer-ab-8-00-bei-athletepharma
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://commuwiki.com/members/jewelfender85/activity/16285/
%random_anchor_text%
References:
https://hikvisiondb.webcam/wiki/Comprar_Anavar_10_mg_comprimidos_Dragon_Pharma_en_Espaa
rob riches steroids
References:
https://dressfifth0.werite.net/dianabol-cure-effets-risques-et-alternative-au-steroide
how does the abuse of anabolic steroids affect teens
References:
https://mozillabd.science/wiki/Top_10_des_meilleurs_complments_alimentaires_pour_maigrir_du_ventre_rapidement_et_efficacement
female bodybuilder steroids
References:
https://marvelvsdc.faith/wiki/Esteroides_Dianabol_Los_efectos_la_compra_y_venta_del_Dianabol_DianabolSteroids_com
maximum male supplement
References:
https://md.un-hack-bar.de/s/caxcU7UyAY
deca durabolin cycle for beginners
References:
https://www.lanubedocente.21.edu.ar/profile/whitleyfuohaslund71143/profile
References:
Las viejas casino
References:
https://www.fionapremium.com/author/bodyeggnog2/
References:
Live casino md
References:
https://humanlove.stream/wiki/Fullsized_Cocktail_Table_Arcade_Game_with_60_Classic_Games
References:
George thorogood i drink alone
References:
https://opensourcebridge.science/wiki/Online_Slots_345_Bonus_200_Free_Spins
References:
Casino android
References:
https://humanlove.stream/wiki/Candy96_Casino_Australia_Your_Premier_Gaming_Destination_Down_Under
References:
Blackjack mountain
References:
https://scientific-programs.science/wiki/Your_Ultimate_Online_Casino_Experience
References:
Century casino edmonton
References:
http://downarchive.org/user/banglehate25/
References:
Toy slot machine
References:
https://nerdgaming.science/wiki/No_Deposit_Bonus_Codes_2026_Free_10_50_Spins_at_CandyLand
References:
How do slot machines work
References:
http://community.srhtech.net/user/edgetomato1
References:
Slots uk
References:
https://www.garagesale.es/author/sampanlunch0/
References:
Casino crush
References:
https://pattern-wiki.win/wiki/Mobile_Access_to_All_Your_Favorite_Games
References:
El cortez casino
References:
http://jobs.emiogp.com/author/oaktights3/
References:
No deposit sign up bonus
References:
https://dokuwiki.stream/wiki/96_1_The_Rocket_WRKH_Mobile_AL_Listen_Live
creatine vs steroids
References:
https://newmuslim.iera.org/members/lookpuppy6/activity/430603/
best supplements to get big and ripped
References:
https://www.giveawayoftheday.com/forums/profile/1598382
legal steroids com
References:
https://bookmarkzones.trade/story.php?title=complements-alimentaires-definition-utilisation-precautions
best steroids for strength gains
References:
http://downarchive.org/user/townteller66/
References:
Elencasino
References:
https://morphomics.science/wiki/1Go_Casino_berprfung_1GoBewertungen_und_SpielerFeedback
References:
Slots casino
References:
https://telegra.ph/Casino-Free-Spins-2026-Casino-Freispiele-ohne-Einzahlung-01-29-2
References:
Reef casino cairns
References:
https://clay-odonnell.thoughtlanes.net/leitfaden-fur-die-besten-exklusiven-casino-boni-casino-boni
References:
Celtic casino
References:
http://ezproxy.cityu.edu.hk/login?url=https://online-spielhallen.de/200-casino-bonus-2025-dreifaches-startkapital/
References:
Slot machine winners
References:
https://maps.google.ml/url?q=https://online-spielhallen.de/1go-casino-aktionscodes-ihr-schlussel-zu-exklusiven-vorteilen/
References:
Online betting sites
References:
https://cameradb.review/wiki/1Red_Casino_Deutschland_VIPSpielpfad_mit_200_Bonus
References:
Blackjack fireworks
References:
https://dohn-flores-2.mdwrite.net/cashback-casino-bonus-die-besten-angebote-2026
References:
How many casinos are in las vegas
References:
https://www.marocbikhir.com/user/profile/547362
References:
Ok casinos
References:
https://pattern-wiki.win/wiki/Best_Instant_Payout_Casinos_Australia_2026_Fast_Withdrawal_Sites
References:
Online dating site
References:
http://exploreourpubliclands.org/members/flatcrate50/activity/1131234/
References:
Aqueduct racetrack casino
References:
http://semdinlitesisat.eskisehirgocukduzeltme.com/user/bluejelly09/
where to buy anabolic steroids online
References:
https://notes.bmcs.one/s/5Bfxtjyyu
stroid use
References:
https://graph.org/Home-02-04-14
insane body builders
References:
https://saveyoursite.date/story.php?title=dianabol-dbol-for-sale-2025-best-legal-dbol-pills-cycles-stacking-guide
steroid user before and after
References:
https://securityholes.science/wiki/All_About_HGH_Injections_Uses_Benefits_and_Precautions
References:
Sbg global mobile
References:
http://semdinlitesisat.eskisehirgocukduzeltme.com/user/copyliquid00/
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
deca durabolin stack
References:
https://www.udrpsearch.com/user/spadegold4
steroid to lose weight fast
References:
https://onlinevetjobs.com/author/turretletter2/
legal injectable steroids
References:
https://coolpot.stream/story.php?title=winstrol-50mg-online-kaufen-mit-diskreter-lieferung-in-deutschland
steroid men
References:
https://p.mobile9.com/davidfox4/
legal steroids .com
References:
http://okprint.kz/user/nuttiger1/
purchasing steroids
References:
https://chessdatabase.science/wiki/Buy_Steroids_Online_in_USA
steroids chart
References:
http://jobs.emiogp.com/author/chessepoxy4/
legal natural drugs
References:
http://dubizzle.ca/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=138184
do steroids burn fat
References:
https://sonnik.nalench.com/user/radishcreek9/
massive testo price
References:
http://king-wifi.win//index.php?title=tonnesenwilhelmsen7831
over the counter peds
References:
http://jobboard.piasd.org/author/lyricpanty8/
best steroids for muscle gain and fat loss
References:
https://forum.dsapinstitute.org/forums/users/galleyblue6/
fast muscle growth pills
References:
https://www.udrpsearch.com/user/pestwine2
best supplements for men to get ripped
References:
https://may22.ru/user/israelwine3/
extreme steroids
References:
https://elearnportal.science/wiki/Anaca3_votre_gamme_minceur
best legal steroids reviews
References:
https://swaay.com/u/xippushvfqk54/about/
anabolic define
References:
https://onlinevetjobs.com/author/slopestreet12/
before and after steroids 6 weeks
References:
https://bradford-upchurch-2.mdwrite.net/oxandrolone-anavar-avex-pharma-100-tabletten-x-10-mg
is androgen a steroid
References:
https://swaay.com/u/ipennyuelrs88/about/
why do anabolic steroids differ from other illegal drugs?
References:
https://robertson-hendriksen-4.technetbloggers.de/oxandrolone-anavar-10-mg-tab-100-tabs
steroid without side effects
References:
https://urlscan.io/result/019c31e2-6eac-711e-bb8f-3d5ee2461860/
powerlifting supplement stack
References:
http://jobs.emiogp.com/author/indiaborder48/
supplement that burns fat and builds muscle
References:
https://dreevoo.com/profile.php?pid=1067269
different types of steroids and what do they do
References:
https://fakenews.win/wiki/The_Ultimate_Guide_to_Anavar_Buying_Prices_and_Cycles_Info
what does androgenic mean
References:
https://www.youtube.com/redirect?q=https://anonyme-miniholiker.de/images/pgs/testosteron_steigern.html
hafþór júlíus björnsson steroids
References:
https://lovebookmark.win/story.php?title=buy-anavar-50-online-uk-steroids-supplements
steroid testosterone
References:
https://empirekino.ru/user/pajamaskiing8/
anavar before and after 1 month
References:
https://urlscan.io/result/019c32ee-8192-728a-bb44-707e20ca6e7f/
steroids buy
References:
https://bom.so/YpEzGI
gear pro steroids
References:
https://lovebookmark.date/story.php?title=how-to-take-anavar-tablets-a-beginners-guide
world abs pro stack
References:
https://yogicentral.science/wiki/Anavar_10mg_MediChem_Kaufen_legale_online_zum_Preis_68
injectable steroid cycles for sale
References:
https://sabinedangel.de/index.php?/archives/60-Alltagsmaske-selbst-sticheln.html
wheeling casino
References:
https://sommer-architekt-warstein.de/VPB-Expertenrat;focus=TKOMSI_com_cm4all_wdn_Flatpress_22800952&path=?x=entry:entry230920-155243%3Bcomments:1
global gaming expo
References:
https://socialbookmarknew.win/story.php?title=online-casino-mit-den-schnellsten-auszahlungen-in-deutschland
blackjack strategy chart
References:
https://bookmarking.stream/story.php?title=instant-casino-online-login-registrierung-casino-konto-anmelden
casino winners
References:
https://linkvault.win/story.php?title=trustly-casinos-2026-warum-instant-banking-traditionelle-methoden-schlaegt
gamble house pasadena
References:
https://peatix.com/user/28986686
silver sands casino
References:
https://notes.io/eaC2w
holland casino online
References:
https://firsturl.de/zCWF420
pink floyd live in venice
References:
https://linkvault.win/story.php?title=best-online-pokies-australia-2026-real-money-sites
liberty slots casino
References:
https://invastu.kz/user/knifehat28/
safe online casino
References:
https://king-bookmark.stream/story.php?title=free-100-pokies-no-deposit-sign-up-bonus-2025
paragon casino marksville la
References:
http://uchkombinat.com.ua/user/fireclover00/
casino la vida
References:
https://p.mobile9.com/suithome96/
cinema casino auxerre
References:
https://gpsites.stream/story.php?title=100-no-deposit-bonuses-at-australian-online-casinos-in-2026
operation blackjack
References:
https://torino.com.mx/user/chordmen80/
ipad casino
References:
https://numberfields.asu.edu/NumberFields/show_user.php?userid=6536469
best casino bonus
References:
https://a-taxi.com.ua/user/shopbreath2/
slots of vegas no deposit bonus codes
References:
https://shenasname.ir/ask/user/davidwoman2
buffalo run casino miami ok
References:
https://linkvault.win/story.php?title=fair-go-casino-progressive-jackpot-pokies-guide
roulette betting system
References:
https://analnoe.com/user/organarcher9/
best online casinos
References:
https://rowe-willard-5.blogbright.net/mr-o-casino-review-115-free-chip-bonus-available
pennsylvania casinos
References:
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/2363897/carrillo-dwyer
wolf run slot machine
References:
https://a-taxi.com.ua/user/asiapin1/
the meadows casino
References:
https://marvelvsdc.faith/wiki/Mr_O_Casino_No_Deposit_Bonus_100_Free_Chip
black jack rules
References:
https://moparwiki.win/wiki/Post:Premier_Crypto_Gaming_with_Fast_Payouts_Fair_Play
blackjack switch
References:
https://hikvisiondb.webcam/wiki/CryptoFriendly_Gaming_Experience_With_NoRules_Bonuses
no deposit poker bonus
References:
https://saveyoursite.date/story.php?title=mr-o-casino-bonuses-from-no-deposit-offers-to-vip-rewards